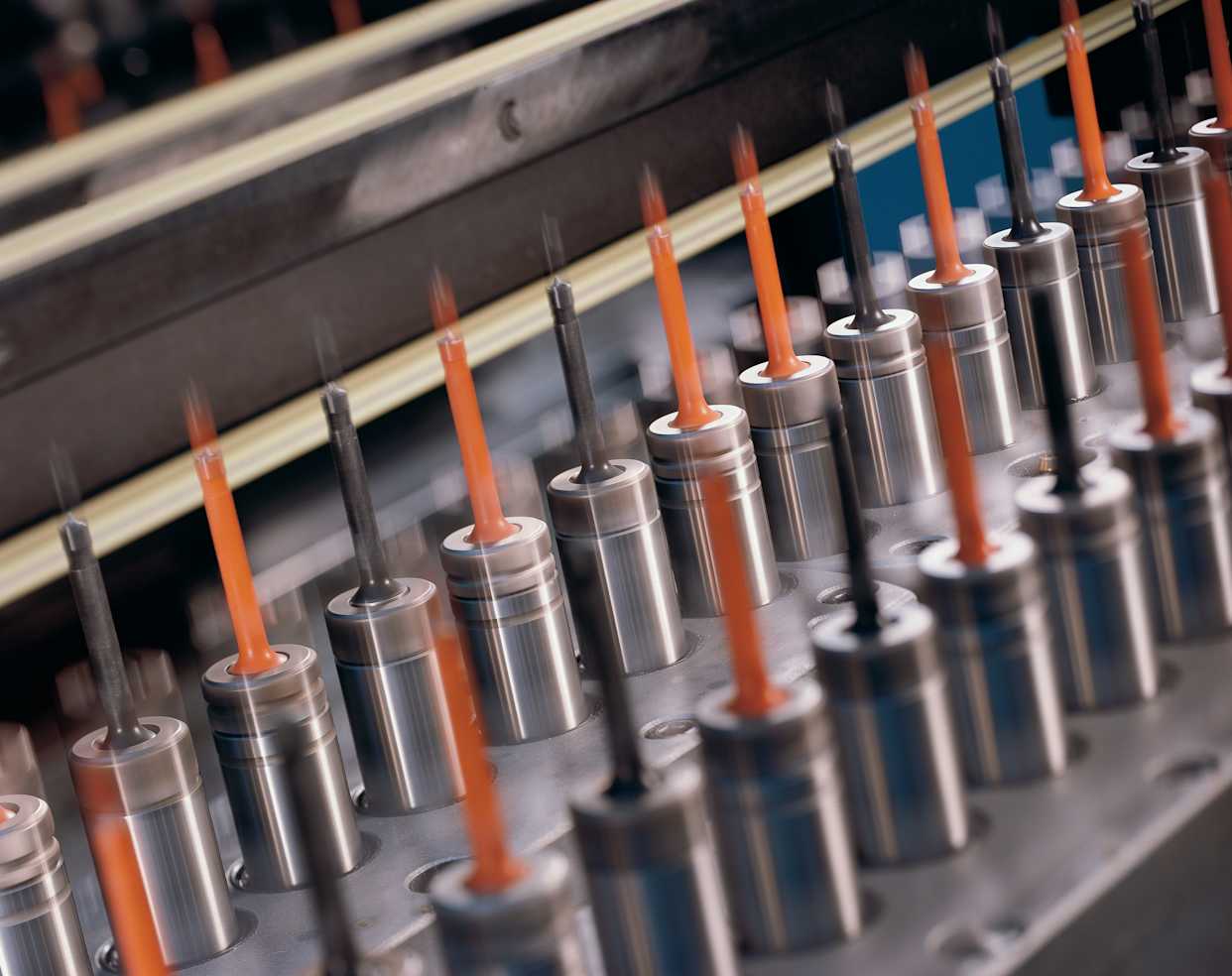

Through this article, you will learn what is meant by reaming and discover the most suitable types and tools for this type of machining. Additionally, we will help you identify the best technology to implement this process. Reaming is a machining process used to achieve precise and regular internal surfaces within a raw workpiece. This process, performed manually using reamers or with a machine, using a manually or automatically operated boring machine, is often carried out to improve the surface finish, internal dimensions, and shape of holes or cavities in various materials such as wood, metal, and plastics.
Reaming operations
Reaming operations on CNC machines are used to finish holes to precise diameters and improve the surface finish of an existing hole. “Reaming” is a machining process that involves the use of a multi-edged cutting tool, known as a reamer, to enlarge a previously drilled, bored, or cast hole. The primary goal of reaming is to achieve a high degree of accuracy in terms of hole diameter and to improve the surface finish.
Types of reamer
Reaming can be done in two ways: using a machine or manually. The choice between these two methods depends on several factors, such as the complexity of the work, the required specifications, the necessary precision, and the quantity of pieces to be processed.
Hand reamers
Hand reamers are tools characterized by an elongated initial part, which facilitates the start of the process, allowing for a more immediate entry into the hole. The manual or hand reamer is multi-edged, distributing the cutting force across all teeth and automatically centering inside the hole.
Machine reamers
Reaming carried out by means of a machine tool involves executing the process using an industrial machinery where the reamers have a smaller body with a tapered initial part (compared to manual tools), ensuring high precision in locating the hole to be worked on.
Tapered reamers
Tapered reamers feature a gradual increase in diameter along their cutting length, starting from a smaller diameter at the tip to a larger diameter at the cutting end. These tools are designed to precisely shape and size tapered holes, typically for fitting tapered pins or achieving specific angle requirements in mechanical assemblies. They are are available in various sizes and taper angles to accommodate different requirements, ensuring that they can match the specific needs of a project or application accurately.
Adjustable reamers
Adjustable reamers, also known as expansion reamers or adjustable hand reamers, are versatile cutting tools used for enlarging and finishing holes to precise dimensions. They are designed with a set of blades or cutting edges that can be adjusted to achieve different diameters within a specified range.
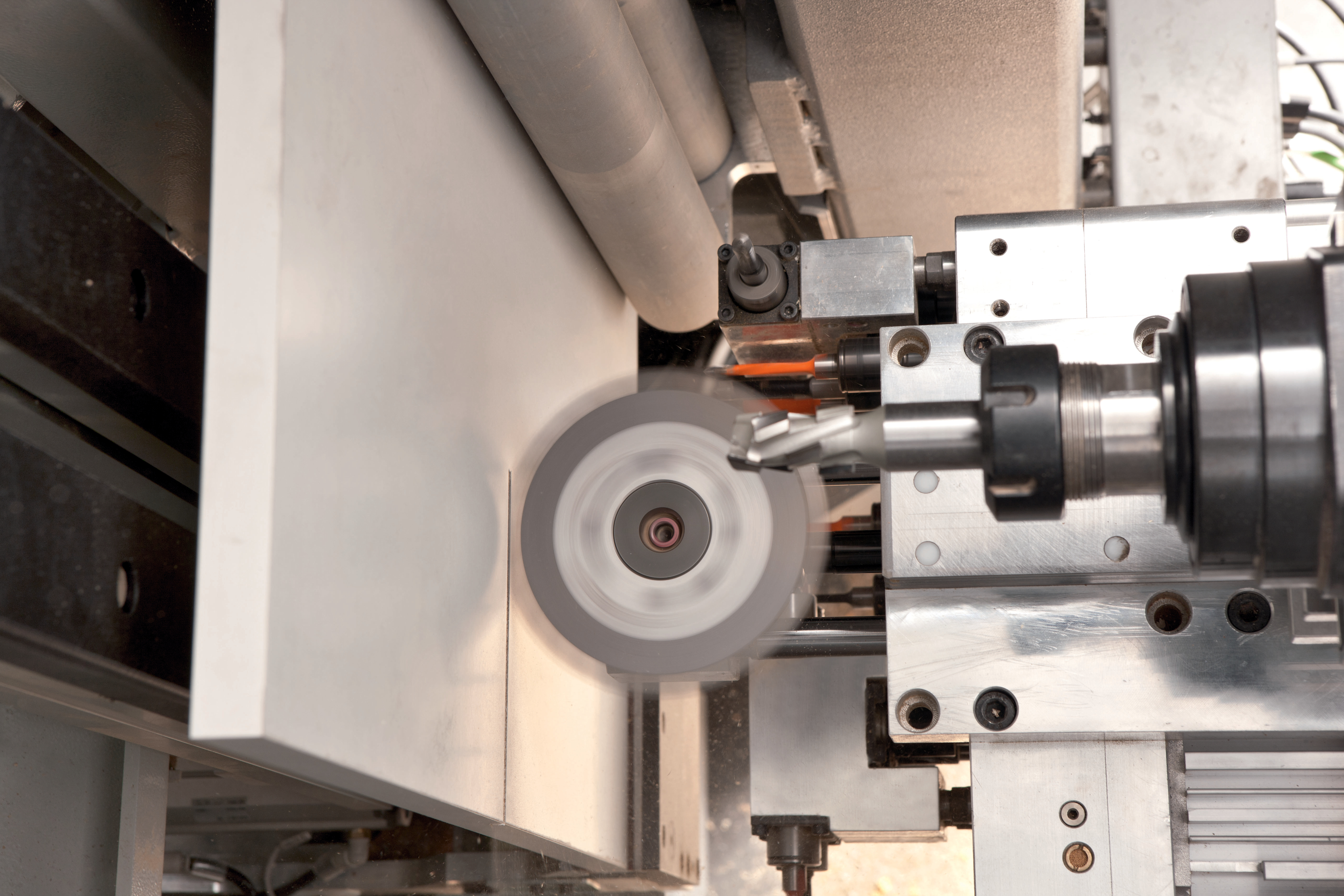
The process of reaming
During the reaming process, a rotating cutting tool called a reamer is rotated and fed into the raw workpiece. The reamer can be mounted on a reaming machine that controls the cutting movement in a precise manner. This process can also be used to correct hole axiality and diameter, as well as to modify and refine internal surfaces, creating high-quality holes with very precise tolerances, crucial in many industrial sectors, such as aerospace and automotive industries.
The applications of reaming
Reaming finds wide application across various industries due to its ability to achieve precise dimensions and smooth surface finishes in machined holes.
Precision hole sizing
Precision hole sizing is crucial for achieving optimal performance, functionality, and reliability of machined components across various industrial applications. It involves careful selection of tools, meticulous machining techniques, and thorough quality assurance processes to meet stringent requirements for dimensional accuracy and surface finish. It can be achieved using specialized tools such as reamers, boring tools, and CNC machining centers. Each tool is selected based on the material, hole size requirements, and desired tolerances.
Hole finishing
Hole finishing is a critical machining operation that ensures holes in machined components meet precise dimensional specifications and surface finish requirements. Hole finishing is important in industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical devices, electronics, and precision engineering. Examples include engine blocks, cylinder heads, transmission housings, printed circuit boards (PCBs), and surgical instruments, where precise hole dimensions and surface finishes are critical for performance and reliability.
Removing burrs
Removing burrs is a process that involves eliminating small, unwanted projections of material, often left after machining operations like drilling, milling, or punching. Burrs can affect the functionality, appearance, and safety of machined parts. This process can be done using hand tools such as files, abrasive pads, deburring knives, or scrapers to manually remove burrs from edges or hole surfaces (manual deburring), using specialized deburring machines equipped with brushes, abrasive belts, or tumbling media to automate the deburring process (mechanical deburring), immersing parts in chemical solutions or applying chemical agents that dissolve or soften burrs (chemical deburring) or using a controlled explosion of gas to remove burrs from inside and outside surfaces of parts (thermal deburring), submerging parts in liquid nitrogen or dry ice to freeze and make burrs brittle, followed by mechanical or tumbling methods to remove them (cryogenic deburring) or using electrolytic action to dissolve burrs selectively without affecting the base material (electrochemical deburring).
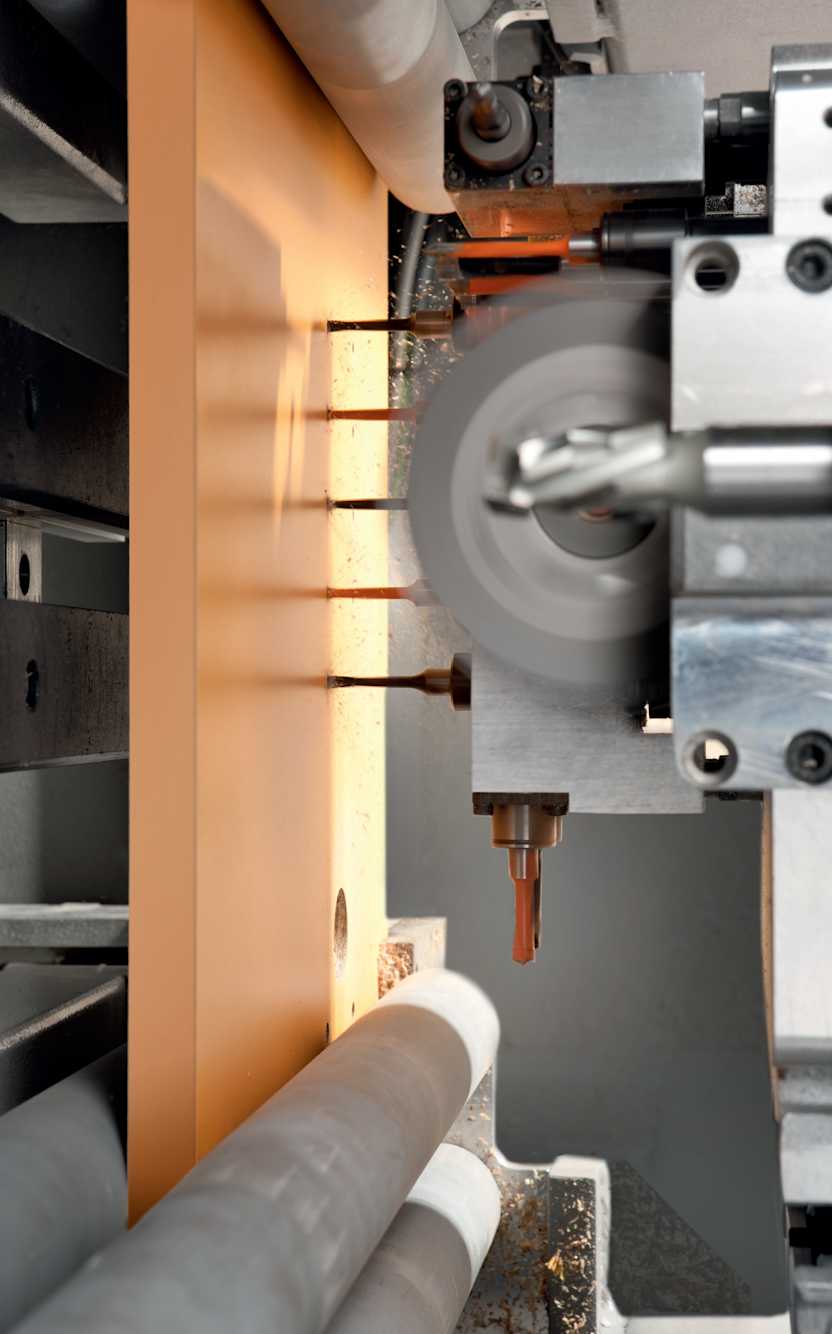

In every work environment, it is important to adhere to specific safety requirements and guidelines put in place to ensure safe operations and processes. Injury risks are associated with falls, impacts, falling materials, contact with moving parts of machines and equipment or sharp edges, entanglement and dragging with working parts, projection of chips during machining, and contact with electrical equipment. Preventive and protective measures include cleaning floors and work areas, maintaining orderliness, and ensuring adequate lighting. Additionally, specific measures, procedures, and operating instructions are required for the setup of plants and machines and for all maintenance operations. Finally, it is necessary to comply with all obligations to wear appropriate clothing and protective gear, to equip the work environment with safety signage, and to prohibit access to unauthorized persons.
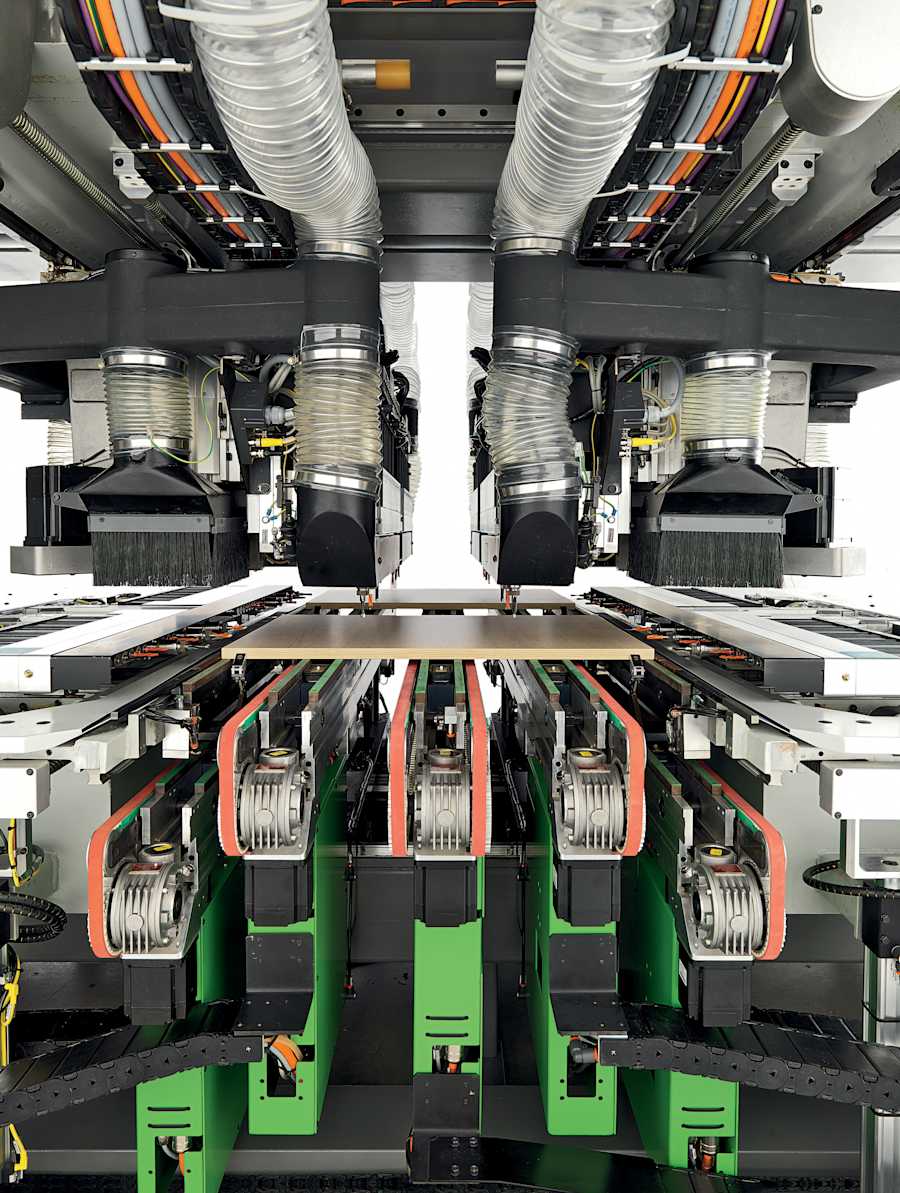
The choice of the right CNC machine for reaming depends on several factors that need to be considered based on the specific production requirements. At Biesse, we offer a range of milling and boring machines that provide a wide selection to meet all production needs: cutting-edge technologies for drilling, milling, routing, and hardware insertion on panels of various sizes. Contact us to discover the boring and inserting machines that best suit your needs.